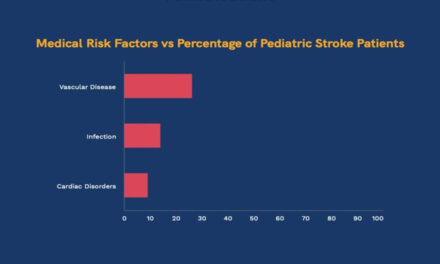
Historically, cerebral palsy was often diagnosed when a child was at least two years old, leading to delays in treatment. However, physicians are now able to diagnose cerebral palsy in children as young as 6 months old by reviewing their medical history along with several reliable tools. Early diagnosis of cerebral palsy is important for several reasons. It can improve motor, cognitive and social development as well as prevent complications that can lead to decreased motor function. An earlier diagnosis can also improve caregiver well-being.
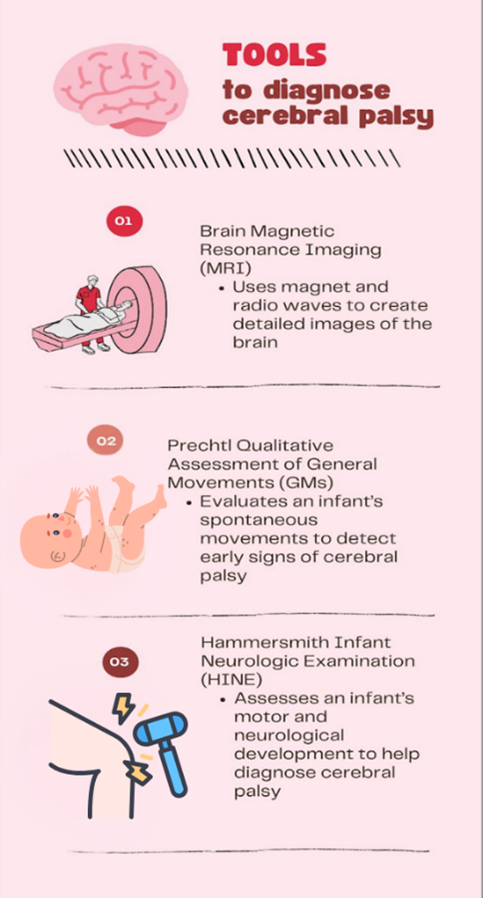
The authors reviewed 8 studies to identify the tools most likely to accurately predict cerebral palsy in infants under 6 months old.
Before 5 months old, the tools that can diagnose cerebral palsy include brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), the Prechtl Qualitative Assessment of General Movements (GMs) and the Hammersmith Infant Neurologic Examination (HINE). After 5 months, the most accurate tools are a brain MRI and the HINE. When unable to access an MRI or assess GMs, the HINE can be used to diagnose cerebral palsy with 90% accuracy.
Despite advancements in early detection of cerebral palsy in infants, the severity and type of cerebral palsy are much more difficult to identify. However, the HINE and brain MRI can provide some guidance to help doctors advise families.
Reference:
Novak I, Morgan C, Adde L, Blackman J, Boyd RN, Brunstrom-Hernandez J, Cioni G, Damiano D, Darrah J, Eliasson AC, de Vries LS, Einspieler C, Fahey M, Fehlings D, Ferriero DM, Fetters L, Fiori S, Forssberg H, Gordon AM, Greaves S, Guzzetta A, Hadders-Algra M, Harbourne R, Kakooza-Mwesige A, Karlsson P, Krumlinde-Sundholm L, Latal B, Loughran-Fowlds A, Maitre N, McIntyre S, Noritz G, Pennington L, Romeo DM, Shepherd R, Spittle AJ, Thornton M, Valentine J, Walker K, White R, Badawi N. Early, Accurate Diagnosis and Early Intervention in Cerebral Palsy: Advances in Diagnosis and Treatment. JAMA Pediatr. 2017 Sep 1;171(9):897-907. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2017.1689. Erratum in: JAMA Pediatr. 2017 Sep 1;171(9):919. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2017.3169. PMID: 28715518; PMCID: PMC9641643.
Abstract Translation: Elana Katz, MD
Graphics: Neha Suresh Ramiah
Medical Editors: Ilona Kopyta, MD
Junior Editor: Christine Zhang